Cohesity and Veritas have joined forces!
See why this is a game changer for the data security space.
Cyberattacks use deceptive tactics to spread across your network. Find elusive threats using AI/ML-driven threat detection thanks to curated threat feeds featuring simple point-and-click threat hunting. Create custom YARA rules to identify advanced threats targeting your environment.
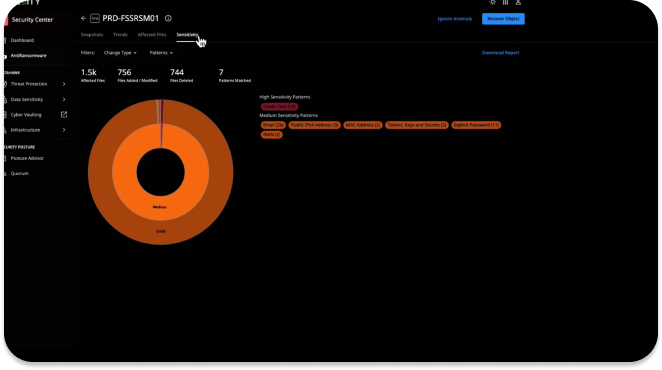
Reduce the risk of reinfection and recover faster using best-in-class threat intelligence curated to address the risk and severity of cyberattacks.
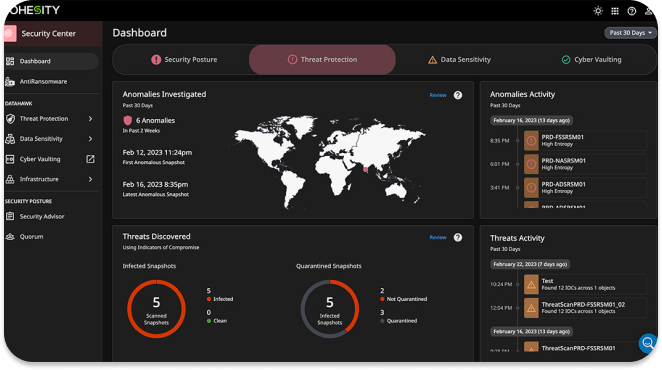
Analyze snapshots with curated threat feeds or create your own YARA rules for elusive threats. Simplify threat protection with one-click threat detection and scanning at scale, and avoid reinfection during recovery.
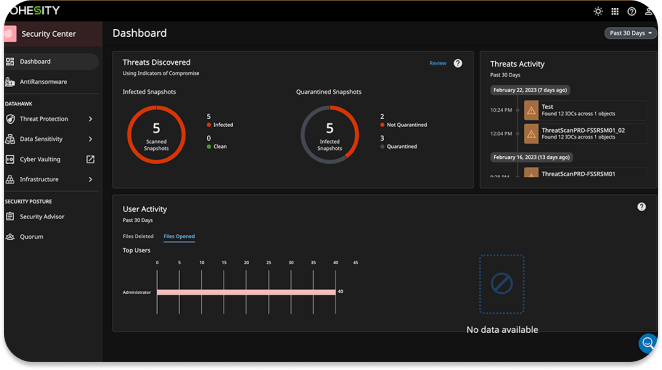
Avoid reinfection during recovery. Perform behavioral analytics to identify malware and threats from malicious insiders. Threat-hunting capabilities allow organizations to identify the early stages of an attack and mitigate it before it has an impact.
Respond faster, recover smarter—because your business can't afford downtime

Threat protection refers to the strategies, tools, and technologies used to defend against malicious software, or malware. Malware includes a wide range of harmful software such as viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, spyware, and adware, among others.
Effective threat protection involves creating an integrated security architecture with several layers of defense, including antivirus software, firewalls, email and web filtering, and patch management. Combined with user education and training, organizations can significantly reduce their risk of falling victim to malware attacks and protect their sensitive data and systems from compromise.
Threat protection safeguards sensitive data from unauthorized access, theft, or corruption. This is vital for protecting both personal and organizational data, including financial information, intellectual property, and customer records. Specifically, malware attacks can lead to financial losses through various means, such as ransom payments, theft of funds, or disruption of business operations. Threat protection helps mitigate these risks by preventing or minimizing the impact of attacks.
Malware attacks will disrupt business operations, leading to downtime, loss of productivity, and damage to reputation. Effective threat protection helps ensure business continuity by minimizing the impact of cyber threats and enabling prompt recovery from incidents. Additionally, many industries are subject to regulatory requirements and standards related to cybersecurity. Implementing effective threat protection helps organizations comply with these regulations, avoiding potential fines, penalties, or legal liabilities. At the end of the day, organizations of all sizes and across all industries must prioritize threat protection to mitigate the risks posed by malware and other cyber threats.
There are many layers of threat protection designed to detect and respond to specific types or stages of an attack. Some examples include:
