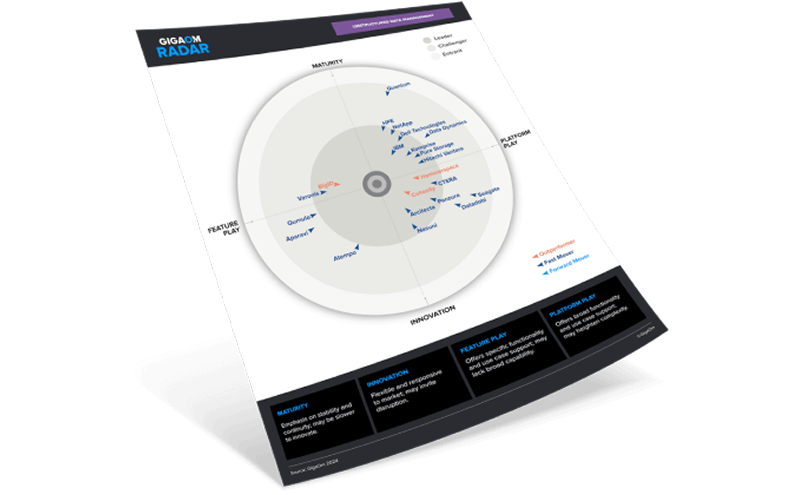
Structured data is data that is stored in a fixed place within a file or record. It’s typically stored in a relational database (RDBMS) but can also be found in NoSQL databases, for example. Structured data can be text, dates, or numbers.
Unstructured data comprises file and object data and has not been defined or stored in a predefined way. Although most common unstructured data consists of text, it can also feature numbers, images, and audio. Unstructured data is used within every function in business. Examples include: Finance (invoices, forms), Healthcare (medical records and images), Public Sector (documents, research data), Manufacturing (design files), Marketing (photos), IT (IoT data), Sales (emails with customers), Customer Service (social media), and more.
Although it’s changing and accumulating rapidly, much of the unstructured data that is collected and stored is processed manually, if at all. For example, email is mostly processed by a human reading it, extracting what is important (sometimes by copying and pasting into another email or into an application), and taking action based on its contents.
But with advancing AI technologies such as machine learning, machine vision, and natural language processing, more of this unstructured information can be harnessed and analyzed automatically, driving faster business insight.